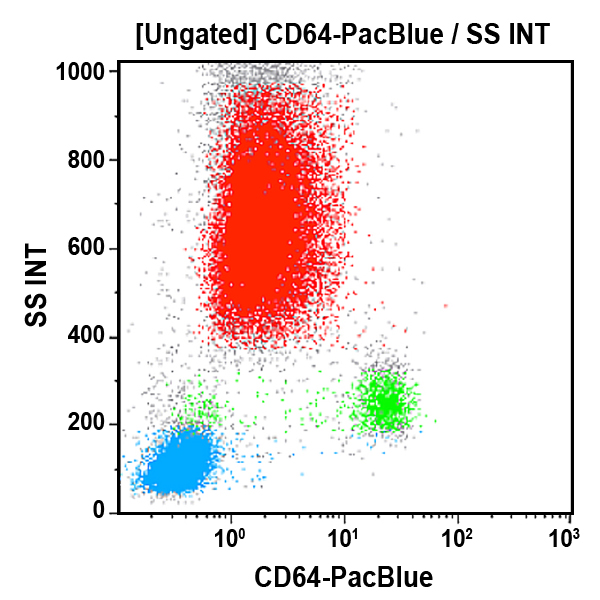
CD64 Antibodies
CD64 is an integral membrane glycoprotein known as an Fc receptor that binds monomeric IgG-type antibodies with high affinity. It is also known as Fc-gamma receptor 1 (FcγRI) or FCRI. After binding IgG, CD64 interacts with an accessory chain known as the common γ chain, triggering cellular activation. Structurally, CD64 is composed of a signal peptide that allows its transport to the surface of a cell, three extracellular immunoglobulin domains of the C2-type used to bind antibody, a hydrophobic transmembrane domain, and a short cytoplasmic tail. CD64 is constitutively found on macrophages and monocytes. CD64 is expressed on early myeloid cells and in IFNγ and G‑CSF activated polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs).
| Clone: 22 | Isotype: IgG1 Mouse |
| The 22 antibody shows especially high affinity binding to human mononuclear phagocytes. The epitope recognized by this antibody is distinct from the IgG binding site. | |